The cause of many diseases, health problems is helminth infection. Various worms can enter the human body. Their sizes range from the smallest millimeters to 16-18 meters. Parasitizing in all organs and tissues, they cause enormous damage to health. To protect yourself from invasion (infection), it is desirable to know what worms are and to understand how you can get infected with parasites of each species.
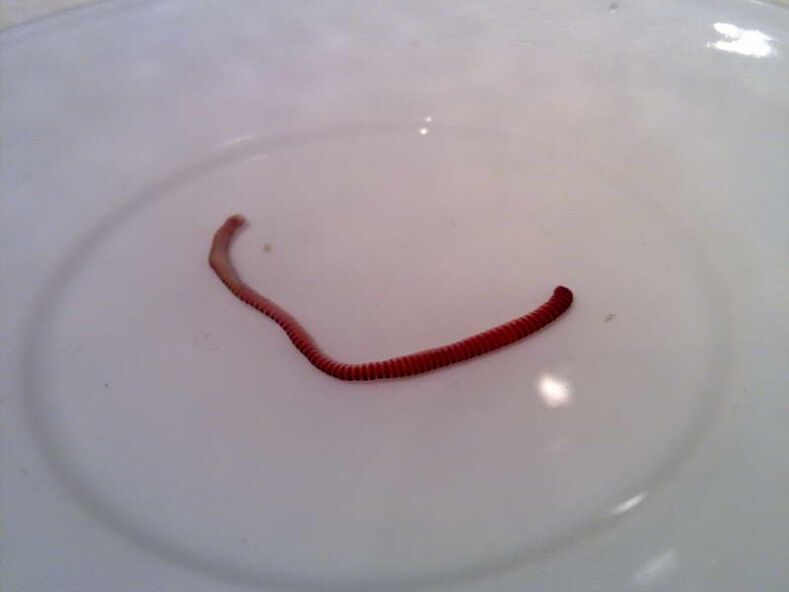

Types of worms - what parasites live in the human body
Depending on the location of the parasitism in the body and the characteristics of the infection, parasites are divided into several classes.
Classification of worms depending on their location in the human body:
- Intestinal- They are worms that live in the gastrointestinal tract, mainly in the small intestine. Sometimes they penetrate other organs. This group includes ribbon and round worms.
- extraintestinal- to develop, live and multiply in different organs outside the intestines. They can be located in the lungs, eyes, brain, liver. This group includes flatworms.
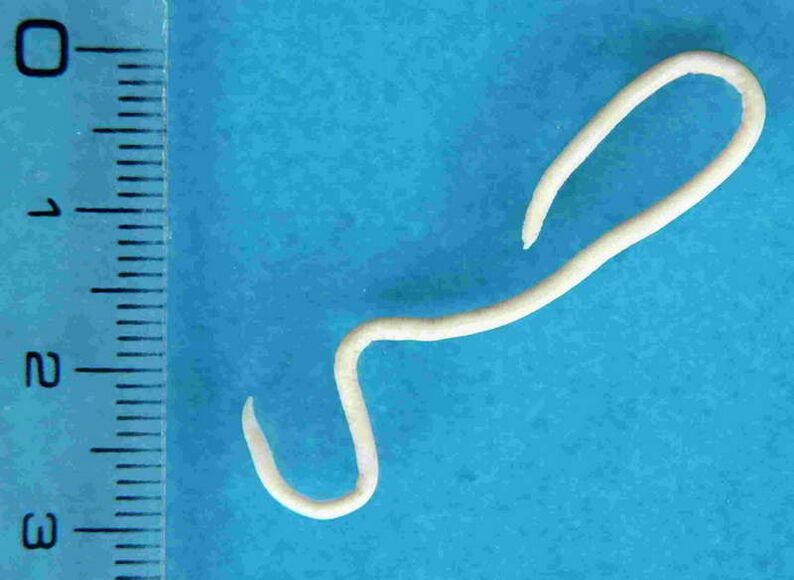
Classification of worms depending on the method of entry into the human body:
- contagious- are transmitted to a healthy person from an infected person during contact. Another source of infection is household items: towels, toys. Representatives of this species are dwarf tapeworm, pinworms.
- Biohelminthiases- are transmitted by contact with an animal, as a result of the consumption of infected meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment. To become potentially dangerous to humans, these parasites must live for a certain period in the body of an animal that is an intermediate host. This species includes bovine and porcine tapeworms.
- Geohelminthiases- part of the life cycle is carried out in the human body and part - in the soil. This is a necessary condition for its development. You can get infected through poorly washed vegetables and fruits. This group includes roundworms, trichinae.
Depending on biological characteristics, helminths are divided into three types - roundworms, tapeworms and worms.

Roundworms (nematodes)
Roundworms are so called because their bodies are round in cross section. These parasites are most often found in a child's body. This type includes:
- earthwormsThey parasitize in the large and small intestine. The body length does not exceed 1 cm. Most often, helminthic invasion by worms affects children. These parasites live for 1-2 months. If you strictly observe personal hygiene, you can recover even without taking medication. If not observed, reinfection is possible.
- worm- worms up to 45 cm long, which parasitize in the small intestine. They can move freely within the intestines. Its life expectancy is 14 months. During this period, they release toxins into the blood, systematically poisoning the body.
- vlasoglav- worms, whose body length is 3-4 cm. They parasitize in the greater and cecum, digging into its mucous membrane to suck blood. Very toxic. Live up to 5 years.
- Trichinella- a parasite with a valley of 3 to 4 mm, which can be infected by meat that has undergone insufficient heat treatment. Helminths live in different organs, settling in the muscles of the eyes, heart and lungs. Life expectancy - up to 2 years.
- hookworm and necator- have the same biological characteristics, development cycle and method of parasitism, so they are combined under the same name "hookworms". These 10 to 15 mm long helminths are located in the duodenum 12. Enter the human body through the skin in contact with contaminated soil. They feed on blood by biting the blood vessels, which leads to iron deficiency anemia. This parasite is difficult to identify.
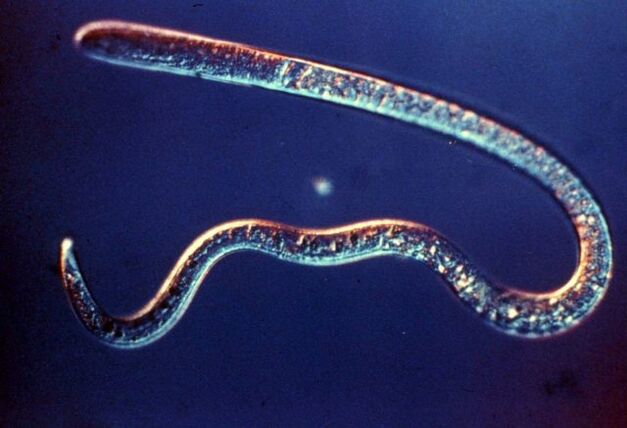
Tapeworms (cestoids)
The tapeworm has a flat body that is divided into segments. As the worm grows, the segments separate from the body and pass out with the feces. These ribbon-like individuals are up to 20 m long. They parasitize in the intestines, where they attach themselves to its walls with the help of suction cups.
To infect humans, tapeworms must go through one of the stages of development in an animal's body.
These parasites live in the body for years. Members of this group:
- wide ribbon- reaches a length of up to 20 m. Parasite in the small intestine, causing severe dysfunction of the digestive tract. You can become infected by eating the flesh of freshwater fish and crayfish that have not been heat treated.
- bull tapeworm- a helminth 6 to 12 m long. It lives in the small intestine, attached by suction cups to its mucous membrane. The source of infection is beef that has not undergone adequate heat treatment.
- pork tapeworm- a parasite up to 2 m long, which enters the body through raw or poorly processed pork. It attaches to the walls of the small intestine.
- echinococcus- a parasite that can be infected by cats, dogs. A person is an intermediate host for this helminth, therefore, entering the body, the larvae penetrate tissues, any organ, and form echinococcal cysts. They are removed exclusively by surgery.
- alveococcus- a type of echinococci. Very dangerous helminths that can live in any organ, but mainly parasitize the liver. They actively grow and develop according to the principle of cancer metastases, gradually infecting the entire body. The worms can be surgically removed.
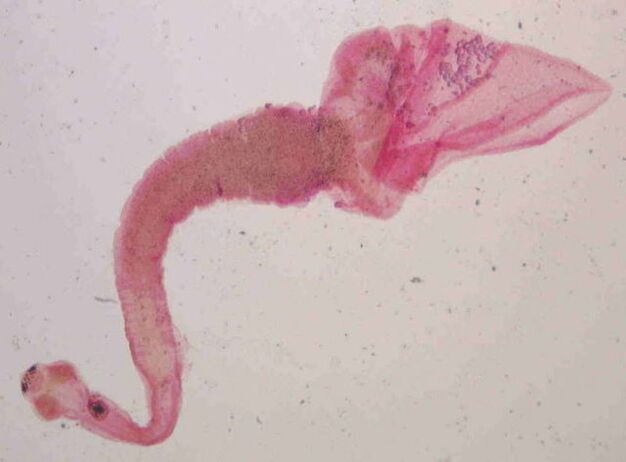
Flukes (trematodes)
Flukes are a type of worm that parasitize any organ and tissue. They feed on epithelial cells. They reach a length of 1. 5 m. The body is shaped like a leaf. The route of infection is consumption of raw fish, shellfish or after insufficient heat treatment. This type includes:
- liver worm- an auger 7–20 mm long. Parasite in liver and bile ducts. It causes the development of serious diseases and functional disorders.
- fluke- a worm 4-13 mm long, located in the gallbladder.
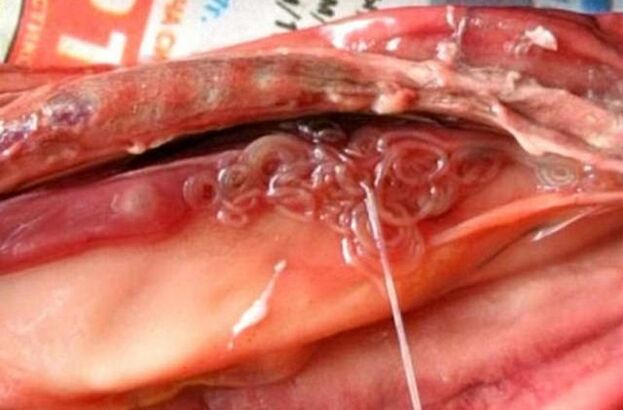
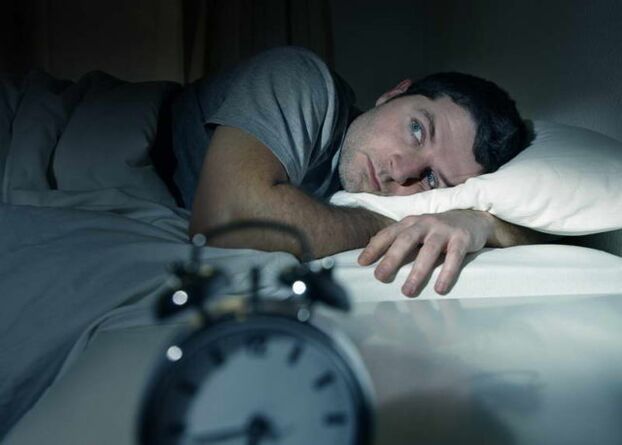
Symptoms - signs of worms in humans
How exactly helminthiasis manifests itself depends on the type of worms that have affected the body and their number. The main symptoms of helminthic invasion:
- diarrhea or constipation;
- bloating, flatulence;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- anemia;
- Allergic reactions;
- dermatitis;
- weight problems - weight loss or obesity;
- sleep disorders;
- nervousness, irritability, depression;
- apathy, fatigue;
- cough, inflammation of the respiratory tract;
- weakened immunity.

How to determine if there are worms
If symptoms appear that could indicate the presence of worms, it is worth making a diagnosis. The following tests will help identify parasites:
- Study of faeces.
- Blood test.
- Examination of the secrets of the duodenum 12.
- Analysis of perianal and rectal mucus.
- Ultrasonography, tomography, endoscopy.
You can be sure of the diagnostic result if you pass the analysis 3-4 times with an interval of several days. One analysis is not sufficient to confirm the absence of helminthic invasion.
The human body can affect one type of worm or several at the same time. All of them, regardless of size, cause serious health problems, they are the causative agents of complex chronic diseases that cannot be cured for years. To eliminate the risk of infection, it is necessary to periodically carry out diagnostics and preventive treatment. This is especially true for pet owners.






































